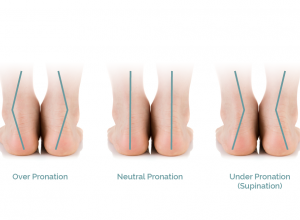
Pronation
Pronation is a naturally occurring movement of the body in which the foot rolls inward to distribute the force of impact of the ground as you walk and run. The movement is a transfer of weight from the heel to the forefoot as you move.
Some people pronate more (called over pronation), others pronate less (called under pronation or supination) and some pronate correctly (called neutral pronation). Over pronating and supination can be potentially harmful and lead to foot disorders.
Neutral Pronation
Normal pronating occurs when the heel strikes the ground, the foot rolls inward about 15 percent as your weight transfers from the heel to the forefoot, and your body weight is supported properly. The foot then continues to push off evenly from the front of the foot. This is your body’s natural method of shock absorption.
Over Pronation
Over pronating occurs when the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward more than the ideal 15 percent. Shock absorption is minimized and the foot and ankle may have trouble stabilizing the body. The foot then continues to push off from the big and second toes, rather than evenly like it should.
Over pronation can cause injuries like Achilles tendonitis, bunions, plantar fasciitis and runner’s knee.
Under Pronation (Supination)
Under pronation occurs when the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls less than the ideal 15 percent inward. Forces of impact are distributed more to the outside of the foot, and the foot continues to push off from the small toes, rather than evenly.
Under pronation can lead to injuries like iliotibial band syndrome, Achilles tendonitis and plantar fasciitis.
An easy way to see if you are pronating correctly is to examine your athletic shoes. If there is excessive wearing on the inside part of the soles, you are probably over pronating. If there is excessive wearing on the outside part of the soles, then you may be under pronating. Both types of improper pronation require extra stretching before physical activity, proper athletic shoes and possibly orthotics (orthoses) to reduce the possibilities of injuries and foot ailments.
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.









