Dermatophyte
Dermatophyte is a fungus that requires keratin for growth. There are three groups of dermatophytes made up of about 40 species, all of which invade the skin, hair and nails. 70 percent of dermatophytes found in humans are from the species Trichophyton rubrum.
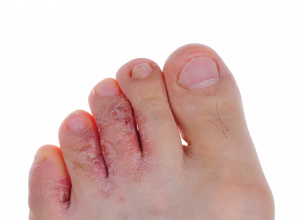
Dermatophyte fungi feed on the nutrients in keratin, which is found in human and animal hair, skin and nails. The most common types of dermatophyte infections include athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), ringworm (tinea corpora) and onychomycosis (tines unguium or fungal infection of the nail).
Dermatophytes can be transmitted via direct contact with an infected host (both human and animal), as well as direct and non-direct contact with items such as hairbrushes, bed linens, clothing, and furniture (which can contain infected hair and shed skin cells). Dermatophytes can also be caught via damp places like saunas, locker rooms and gyms.
Treatment of fungal infections caused by dermatophytes varies from topical medications like miconazole, clotrimazole and terbinafine, and oral medications like fluconazole, itraconizole and griseofulvin.
Dermatophyte infections on the fingernails and toenails are especially difficult to treat. They may need more aggressive treatments like laser therapy.
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.