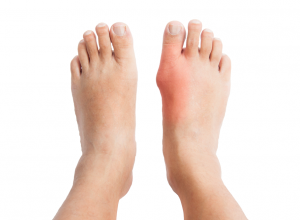
Splay Foot
Splay foot is a deformity characterized by broad, flat feet that oftentimes turn outward like duck feet. The condition happens when the metatarsal bones begin spreading out like a fan, leading to a widening of the forefoot.
Symptoms
People who have splay foot generally experience load-dependent pain while walking and standing. The pain usually dissipates while resting or relieving weight from the foot.
READ MORE: How To Tell If You Have Splay Foot
Because splay foot causes certain parts of the foot to carry the body’s weight improperly, painful corns, calluses and sores can develop and interfere with the rolling mechanism of the foot.
As splay feet are extra wide, it can be difficult for people with affected feet to find comfortable shoes.
Causes
While an exact cause of splay foot is unknown, most medical specialists agree that it usually develops following several years of improper strain on the foot from obesity, ill-fitting shoes, high heeled shoes or prior conditions or injuries that affected a person’s natural gait. Over time, the transverse bulge of the foot begins to disappear and the forefoot broadens.
Splay foot is said to be the most common foot deformity, next to bunions (hallux valgus).
Treatment
Conservative treatment of splay foot is most often prescribed, and it includes wearing orthopaedic inserts or orthoses, as well as engaging in exercises that strengthen the calves, ankles and foot muscles, which will help alleviate the pain and discomfort that often accompanies the condition.
People with splay foot are advised to avoid excessive strain on the forefoot and to frequently alternate any foot and leg exercises. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain killers can also be taken.
If left untreated, splay foot may lead to bunions, hammertoes and claw toe.
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.







