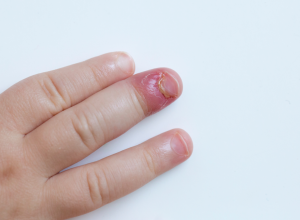
Paronychia
Paronychia is a bacterial infection of the hand or foot where the skin and nail meet. The infection often shows itself as red, painful swelling near where the skin meets the nail.
Symptoms
Paronychia can start suddenly (acute paronychia, which lasts less than six weeks), or it can appear gradually over time (chronic paronychia, which lasts more than six weeks). Both types show themselves with local redness, swelling and pain on the skin just near the nail, but chronic paronychia can lead to the cuticle separating from the nail plate, leaving the area vulnerable to further infection.
Causes
Acute paronychia is usually caused by minor injury to the cuticle or nail fold. Common activities that lead to acute paronychia include biting or picking at a hangnail, washing dishes, having an ingrown nail, sucking on the fingers or toes, and manicure/pedicure procedures.
Chronic paronychia is often due to contact dermatitis. It is often due to dish washing, cutting the cuticles too short, finger sucking and frequent contact with chemicals (such as those used in cleaning products).
Candidal paronychia is inflammation of the nail fold caused by Candida albicans.
Treatment
According to a study published in the Am Fam Physician by experts D. Rigopoulos, G. Larios, S. Gregorious and A. Alevizos, the best way to treat both acute and chronic paronychia is “warm compresses; topical antibiotics, with or without corticosteroids; oral antibiotics; or surgical incision and drainage for more severe cases.” Furthermore, those with chronic paronychia should avoid exposure to chemicals and other contact irritants in combination with using a broad-spectrum topical antifungal corticosteroid. In rare cases, nail removal may be necessary.
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.







