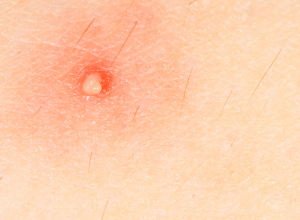
Boils
A boil, also referred to as a skin abscess, is a type of skin infection that begins at a hair follicle or oil gland. They generally start as bumps of red inflammation and gradually develop into tender, pus-filled lumps. The most common places boils are found are on the face, neck, armpits, shoulders and buttocks.
Symptoms
Boils usually begin as a red bump in the skin about an inch in size that gradually becomes larger, softer, more painful and begins to fill with pus (which is a mixture of bacteria, infection-fighting white blood cells and proteins). Sometimes a fever and swollen lymph nodes accompany boils.
Causes
Most boils are caused by the bacteria staphylococcal (Staph), but there are many other causes of the abscesses, including ingrown hairs, splinters and plugged sweat glands that become infected (which produces the type of boil called acne). Anyone can develop boils, but people with weakened immune systems and ailments like diabetes and kidney failure are more susceptible.
Treatment and Prevention
Boils themselves aren’t contagious, but the bacteria found inside of them can spread from person to person through the sharing of personal items and skin-to-skin contact. Common treatment includes application of heat either through warm water soaks or hot packs. The heat helps stimulate blood circulation, which assists the body in better fighting off the infection. It is not recommended that you use a needle to pop the boil, as it can lead to a worse infection. However, once the boil comes to a head (a small pustule is present in the center of the boil), you can drain the boil for pain relief if it is small. For larger boils, it is recommend that you visit a health care provider who can lance the boil and drain it safely.
The best way to prevent boils is to regularly bathe. It’s helpful to use antibacterial soap if you’re physically active or frequently in places where bacteria spreads (gyms, public pools, locker rooms, etc).
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.






